Heat is a normal part of generator operation, but there are times when a generator is under strain without any visible signs. In many cases, the warning signs were there long before the breakdown, but were not obvious to the average operator. Excess heat is often the first signal that something inside the system is off balance. That’s where thermal imaging for critical power systems plays an essential role. It acts as an early warning system that should be part of every preventive maintenance plan.
How Thermal Imaging Works
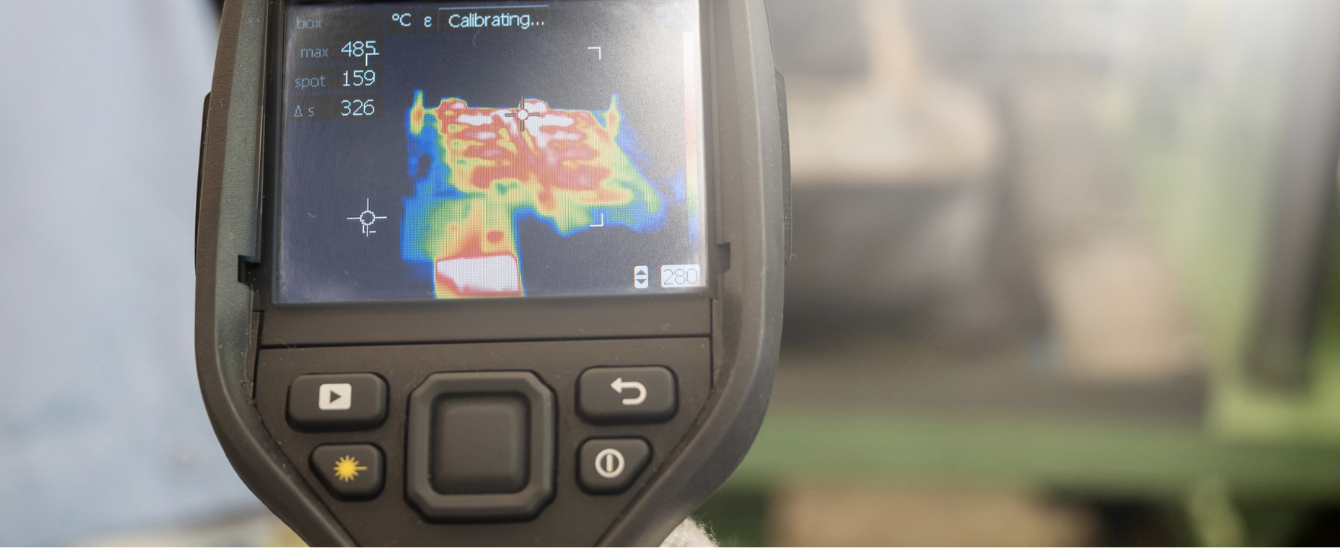
Thermal imaging detects infrared radiation from each component of the generator while it’s in operation. The data collected is converted into a temperature map known as a thermogram. Technicians compare this thermogram to the manufacturer’s standard operating temperatures to locate irregularities.
When certain areas register temperatures above or below normal ranges, it points to potential problems such as friction, electrical resistance, or uneven load distribution. These readings allow maintenance teams to focus directly on the source of the issue instead of guessing where a fault might be.
Thermal imaging is especially valuable because it evaluates the generator while it’s active, not during a shutdown. Some issues, such as voltage imbalance or bearing friction, only appear when the unit is under load. Scanning under real operating conditions gives technicians a true picture of how the generator performs.
Why Thermal Imaging Matters
The main benefit of thermal imaging is early detection. It identifies areas of concern before they result in breakdowns, power loss, or safety hazards. Loose electrical connections, worn bearings, or overworked wiring may not be visible during a standard inspection, but they are easy to spot through heat mapping.
By catching these problems early, technicians can schedule repairs at convenient times instead of reacting to emergencies. This prevents unplanned downtime, avoids damage to expensive components, and reduces the risk of fires caused by overheating electrical parts. The result is safer, more reliable power for the entire facility.
Routine thermal imaging for critical power systems also improves asset longevity. Generators and associated electrical components last longer when they’re maintained at proper temperature levels. The scans provide documentation of equipment health over time, helping maintenance teams track trends and make informed service decisions.
Common Applications
Several parts of a generator benefit greatly from regular thermal imaging inspections. Electrical connections, terminals, and control panels are often the first to show signs of excess heat. These areas can become overloaded or develop resistance that leads to arcing and, in severe cases, fire.
Thermal imaging is also valuable for inspecting bearings, transformers, switchgear, and rotating machinery. Elevated temperatures in these areas indicate stress that could lead to failure if ignored. Identifying these hot spots helps technicians target the exact cause, whether it’s insufficient lubrication, misalignment, or an electrical fault.
Incorporating thermal scans into a routine maintenance schedule allows facilities to maintain performance standards while protecting both people and property from avoidable hazards.
Don’t Wait for a Failure
A generator failure is more than a temporary inconvenience. It can bring production to a stop, affect safety systems, and lead to significant repair costs. Preventive care is always more cost-effective than emergency recovery.
Thermal imaging for critical power systems is one of the most practical ways to prevent those outcomes and keep operations stable.
If your facility is located in Glendale, AZ; Tucson, AZ; Las Vegas, NV; Commerce City, CO; or Albuquerque, NM, GenTech’s technicians are trained to perform detailed thermal imaging inspections and full generator maintenance services.
Stay ahead of potential failures before they happen. Contact
GenTech today to schedule a thermal inspection and keep your power systems operating safely, efficiently, and without interruption.